Desktop applications have been there since the 1990s and have assisted many with their different needs. It is installed in computers as desktop software or applications for different needs or purposes and differs greatly from mobile or web applications.
Today, mobile and web applications are more popular due to the growth in smartphone usage. Desktop applications still offer unique benefits, making them the preferred option for several needs and requirements.
This post provides a complete guide on developing a robust desktop app from beginning to end. We discuss important aspects, such as how desktop applications differ from mobile applications, and outline the growing demand that drives the respective market and the step-by-step development process.
Let’s dive in.
Desktop Application: An Overview
Desktop applications are computer programs run on desktops and laptops. These apps are designed for operating systems such as Windows, macOS, and Linux. The global remote desktop software industry crossed $2.83 billion in the year 2024.
They provide a standalone graphical user interface (GUI) and access device features like files, printers, cameras directly. Examples include MS Word, Excel, Visual Studio, Adobe Photoshop, Xcode, etc. Desktop apps offer various advantages over other digital solutions.
Why Is There a Growing Demand For Desktop Apps?
There has been a rising demand for desktop applications from businesses recently due to their various advantages over web and mobile applications. Desktop apps allow businesses to automate routine tasks and workflows, enhancing productivity and efficiency.
They also offer powerful controls and features tailored to an organization’s specific needs. Desktop software can be customized to integrate seamlessly with other legacy systems and lines of business applications enterprises use.
Businesses leverage the latest technologies through desktop apps to remain competitive in their industries. Furthermore, desktop apps provide businesses with added cybersecurity and data protection layers.
They offer faster performance when handling large and complex data sets than web and cloud-based solutions. With desktop apps, businesses also regain control over their critical IT infrastructure and save costs on additional hardware requirements for mobile and web apps.
Key reasons for the growing importance of desktop apps in businesses include:
- Reduced risks of data breaches and vulnerabilities
- Customizable interactive features as per business needs
- Tighter integration with other internal enterprise systems
- Lower operating costs through automation of routine workflows
- Improved productivity with faster computation of large datasets
- Enhanced data security and protection from external threats
Desktop Application V/S Mobile Application V/s Web Application: What’s the Difference?
If you think mobile applications and desktop applications are more or less similar, than you cannot be more wrong. To make things easy and understandable, we have provided the differences between the two in the table below. Check it out:
Reasons To Choose Desktop Application
There are many advantages to choosing desktop applications over other types of software. Here are the top reasons to consider desktop applications for your needs:
-
Network Independence
Desktop apps can operate without an internet connection, allowing continuous offline access to functionality and data. This is useful when internet connectivity may be unreliable or limited.
-
Safety & Confidentiality
These applications run locally on the user’s computer, keeping sensitive data secure. They don’t support transmitting data over the Internet, making them ideal for handling confidential information and important work.
-
Easy To Access & Control
Users can customize desktop apps according to their specific needs, providing a personalized experience. They also have full control over app settings and preferences.
-
Amazing Compatibility
Desktop apps are designed for compatibility with underlying operating systems and hardware. They can leverage the system’s full capabilities and integrate seamlessly with other software.
-
Less Stringent Hardware Requirements
Desktop apps are developed to run efficiently even on older computers, expanding their reach to a broader audience base. Users do not need the latest hardware to access full functionality.
-
Access to Local Resources
Desktop apps can access local files, devices, and system features – allowing greater functionality like file manipulation, hardware integration, and platform-specific capabilities.
-
Offline Capability
Unlike web and mobile apps, desktop software ensures uninterrupted work even without internet connectivity, protecting productivity in areas with unreliable network access.
-
Increased Performance & Responsiveness:
By fully utilizing local system resources, desktop apps deliver faster processing, smooth interactions, and an optimized user experience. This helps in improving the performance and responsiveness of the desktop application.
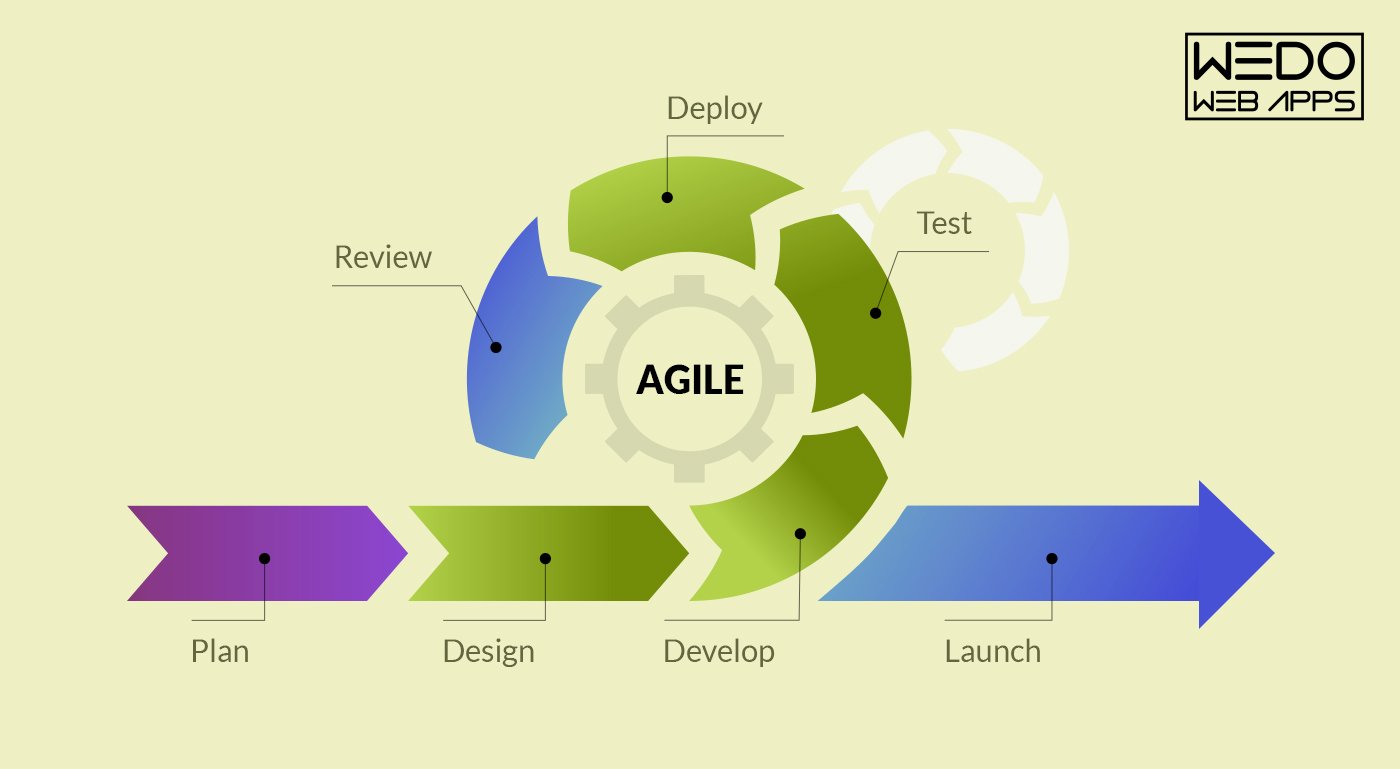
Steps To Make A Desktop Application
Here are the key steps to develop a fully functional desktop application:
Step 1: Define the Application Requirement
This step involves understanding the purpose, features, and target audience and gathering stakeholder input. The requirements are then documented for reference during the development stages.
Step 2: Design The Application
At this stage, the application’s visual interface, navigation flows, interactions, and architecture are planned and prototyped using design tools.
Desktop application development tools that are used for designing:
- Moqups: When it comes to Moqups it is a simple and powerful wireframing and prototyping tool. It is known for developing clickable prototypes and that too without writing any code.
- Mockplus: Mockplus is a versatile prototyping tool that supports collaboration and user testing. It provides various widgets and templates to design interfaces.
- Adobe XD: Adobe XD is a leading design tool that helps bring designs to life with intuitive features for styling interactions and animations.
- Mockingbird: Mockingbird is a full-fledged prototyping software for designing interfaces across platforms quickly with ready components.
This covers the key aspects of designing desktop applications. In the next sections, the steps from programming to deployment are covered.
Step 3: Choosing a Programming Language
Check out the most popular programming languages taken into consideration for developing desktop applications:
- C/C++: C/C++ is a low-level language that provides full access and control over hardware. It is suited for resource-intensive or complex applications.
- C#: C# is used along with the .NET framework, making it ideal for Windows desktop development. It simplifies common tasks with robust libraries.
- Java: Java is highly portable and supports cross-platform development. It ensures applications run seamlessly across systems.
- Python: Python is a versatile scripting language known for simplicity. It has huge libraries support and facilitates rapid development.
- C++: JavaScript combined with Electron framework allows creating desktop apps using web technologies like HTML, CSS for cross-platform distribution.
Each language has strengths based on requirements like performance needs, platform support, etc. Proper evaluation helps choose the right programming language.
Some key factors to consider are:
- OS support: Choose a language supported by target OS platforms like Windows, Mac, Linux to ensure compatibility.
- Capabilities: Consider if the application involves resource-intensive tasks, GUI, performance-critical code, etc which aid language selection.
- Learning curve: Examine the learning effort and community support required for each option to be picked up by the team. Popular choices for desktops include C++, C#, Java, and Python due to their wide skill availability and extensive documentation.
Step 4: Select A Development Platform/ Framework
Frameworks provide pre-built components to accelerate development. Options include Electron for cross-platform JavaScript apps, Qt for C++ GUIs, GTK for Linux, and JavaFX for portable Java interfaces.
Evaluate framework features, documentation, community size, and alignment with requirements and programming language to select the most suitable choice.
Step 5: Install an IDE
An Integrated Development Environment bundles essential tools in one place, boosting productivity. For desktop development in C#, Python, Java, etc., install stable and feature-rich IDEs like Visual Studio, PyCharm, and IntelliJ, respectively.
These IDEs offer code completion, debugging, version control, and build system integration. The IDE streamlines coding, testing, and deployment activities.
Step 6: Create the Application
With prerequisites fulfilled, initiate the coding phase. Progress iteratively – define user interface scaffold using relevant graphical libraries, build application logic through functions and classes, and integrate data model layer for storage and retrieval.
Modularize code into well-designed, portable, and testable units. Routinely commit and back up code. Leverage available framework utilities to maximize efficiency.
Step 7: Testing and Debugging
Thorough testing ensures quality and defect-free software. Create test cases to validate features under varied inputs and edge conditions. Common techniques include:
- Unit testing with frameworks like JUnit – Isolate and automate verification of individual application components.
- Debugging tools and techniques – Simulate runtime errors, evaluate variable states and trace execution flow using IDE debugger and logging to squash bugs efficiently.
Step 8: Packaging and Distribution
Package the application and prerequisites as a standalone installable software bundle for each target platform. This includes:
- Platform-specific installation files – .msi for Windows, .dmg for macOS etc, ensuring compatibility.
- Distribution through app stores or websites – Digital avenues like Microsoft Store, own website introduce the application to a wider audience base leveraging their installation and update services.
Step 9: Maintaining and Updating Apps
This ongoing process strengthens program quality and user satisfaction:
- Version control and release management – Tools like Git facilitates code revisions, feature additions, and rollback through tagged releases.
- Engaging users with update notifications: Communicate new improvements and patches transparently through in-app notes or emails while respecting their choice. Bug squashing through continued testing is crucial.
A methodical, step-by-step approach that considers technical and non-technical factors translates abstract ideas into robust, full-fledged desktop applications loved by users. Regular maintenance keeps software relevant and secure over time.
Popular Frameworks To Develop Desktop Applications
Frameworks accelerate development by providing reusable components and tools. Here are some major options for desktop application development:
-
Electron
- Open source framework for building cross-platform desktop applications using Javascript, HTML, and CSS.
- Build desktop UIs using web technologies and distribute apps through package managers
- Apps like VS Code Slack are built with Electron.
-
WPF
- Microsoft framework for building desktop clients on Windows.
- Develop using XAML for declarative UI creation and C# for logic.
- Provides advanced 2D/3D graphics, media integration, and animations.
- Large community support with tools in Visual Studio.
-
WinForms:
- Microsoft’s oldest framework to create Windows applications in .NET.
- Drag-and-drop interface building with robust controls.
- Simple to learn but lacks the flexibility of WPF’s graphic rendering.
- Used for traditional Windows applications.
-
Cocoa:
- Apple’s native framework for OS X and iOS application development in Objective-C or Swift.
- Access platform APIs and build rich GUIs for macOS.
- Apple’s recommended way of building Mac software.
- Strong development tools in Xcode IDE.
-
Universal Windows Platform (UWP):
- Microsoft’s platform for creating Windows 10 desktop apps and beyond.
- Build once deployed everywhere across Windows, Xbox, and HoloLens.
- Rich features like live tiles, notifications, and in-app purchases.
- Supports JavaScript, C#, Visual Basic, and C++.
Cost of Creating Desktop Applications
Developing professional desktop applications requires substantial investment but offers long-term benefits:
- Depending on complexity, planning and design costs vary from $5,000 to $30,000.
- For a minimum viable app, budget $25,000-$50,000 for a 3-6 month development timeline.
- Adding features, testing, and debugging may increase costs to $50,000-$100,000 on average.
- Maintaining and upgrading apps over the years costs 10-15% of the original budget annually.
- Hiring experienced, dedicated developers costs $50-100 per hour for contracting or $80,000-150,000 annually.
- Overall, development is more expensive than web/mobile, but desktop software has longer life cycles.
Future of Desktop Applications
While cloud-based and mobile applications have seen tremendous growth in recent years, desktop applications will continue to play an important role in the future. According to a survey conducted by SplashData in 2022, over 80% of knowledge workers worldwide still rely on desktop applications daily for their productivity needs.
Some key trends that will shape the future of desktop applications include:
-
Enhanced Security:
With work becoming more distributed and businesses storing sensitive data locally, security will be a major priority for desktop applications going forward. Technologies like application containers and sandboxing will become more widely adopted to isolate potentially vulnerable third-party software and prevent data breaches.
The container market alone is expected to grow at a CAGR of over 25% through 2028 as these technologies provide stronger defense against emerging cyber threats. Leading application developers will focus on building security features like code signing, application shielding and runtime application self-protection natively into their products.
-
Specific Use Cases:
While many routine tasks will shift online, desktop applications are uniquely suited to handle data-heavy workflows that require access to local computing resources.
Creative professionals working with multimedia files, 3D modeling, video/image editing and scientists involved in data analysis will continue relying on desktop software that can harness the full processing power of high-end workstations.
About 45% of the creative/design workforce is forecast to exclusively use desktop applications through 2030 for projects involving very large or complex data sets that would be inefficient to handle in the cloud.
Another area is enterprise/industry use cases like CAD/CAM, lab automation, medical imaging, real-time analytics in manufacturing plant floors which depend on low-latency access to local peripherals, sensors and hardware.
-
Customization and Integration:
Large enterprises have complex and customized business processes spanning different internal departments, and off-the-shelf SaaS may not always meet these specialized requirements.
Top desktop application vendors are focusing on sophisticated customization capabilities like visual workflow/form builders, plug-in architectures and powerful APIs to integrate seamlessly with line-of-business systems, ERPs, industrial equipment, IoT devices as well as customize UX for niche enterprise needs.
Today, companies around the world currently depend on internally customized/developed desktop apps and this trend is likely to continue as businesses demand tightly integrated, configurable solutions tailored for their industry.
-
User-Friendly Interfaces:
To compete with the slick interfaces of mobile/web apps and gaming platforms, desktop UX will see increased innovation around visual design, animations, gesture controls and input modalities to enhance engagement and productivity.
Concepts like Interactive Canvas, Morphic UI, 3D modeling interfaces are opening up new possibilities beyond the traditional window-icon-menu-pointer (WIMP) paradigm.
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) also provide an evolution path for desktop experiences through service workers, responsive design and push notifications.
Most productivity suites and creative tools are expected to adopt contemporary designs inspired by digital illustration/sketching tools, taking advantage of the large displays and input methods on workstations.
-
Offline Access:
While cloud services promise reliable online access in typical office environments, disconnected use cases will remain critical for scenarios involving unpredictable network availability – such as telecommuting, field work, transportation, remote/rural places, emergencies and military applications.
Industries like manufacturing, utilities, aviation, Oil & Gas, that mandate operational continuity even in harsh terrains/conditions will keep requiring robust offline capabilities.
This is likely to drive further investment in innovation around local/peer-to-peer syncing, low bandwidth operation, predictive caching, drawing data from local/embedded databases and optimizing UX for limited functionality without internet connection.
By 2028, desktop apps in sectors requiring airtight operations in disconnected environments are expected to offer full offline mirroring of key cloud services and synchronization once back online.
Conclusion:
Today, desktop applications are used by lots of companies and individuals in their everyday lives. Users use it for a variety of purposes, including accessing the latest information and forecasts for weather as well as managing their finances and playing video games etc.
These applications are also employed by companies, such as banks desktop applications, which give access to accounts of customers and transaction information. Building software is an iterative learning experience.
We hope this guide has provided a good starting point to get you developing exciting desktop applications.
Just keep practicing, learning from mistakes, and ensuring user-centered design in the softwares. This will help you in creating great software in no time that people will love using. However, most importantly, have fun while developing!